Recent studies indicate a troubling trend: cancer diagnoses among adults younger than 50 are becoming more common. What used to be considered an affliction of the elderly is striking more and more people during their prime working and child-rearing years.
“By 2030, one recent study estimated, the number of these early-onset cancer diagnoses could increase by roughly 30% worldwide,” says Dr. Aisha Ahmed, medical oncologist and hematologist at Arizona Oncology. That’s a frightening statistic, but understanding what drives it can be empowering.
Dr. Ahmed walks us through the facts.
Why Are More Young People Developing Cancer?
How many times have you thought, “Cancer doesn’t run in my family, so I’m safe.”? Unfortunately, that isn’t the case. The uptick in cancer diagnoses in younger people is tied to lifestyle factors and the environment, not genetics.
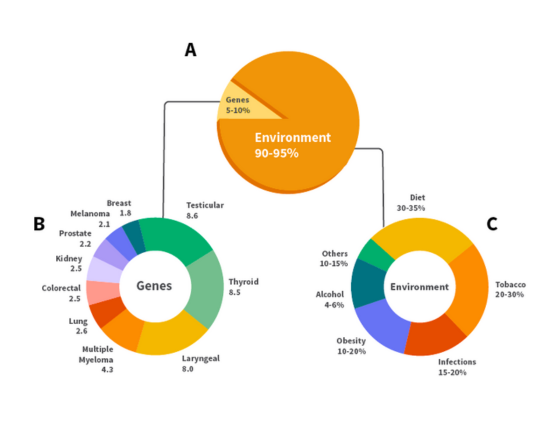
“Only 5–10% of all cancer cases can be attributed to genetic defects, whereas the remaining 90–95% have their roots in the environment and lifestyle,” says Dr. Ahmed. These key environmental and lifestyle factors include:
- Environmental Pollutants: Exposure to microplastics and chemicals.
- Dietary Habits: Consuming large amounts of processed foods.
- Lifestyle Choices: Sedentary behavior, lack of exercise, increased alcohol consumption, and smoking.
- Obesity: Linked to several types of cancer, obesity rates are rising among younger populations.
- Chronic Stress and Poor Mental Health: Modern life pressures, including work, education, and social factors, can increase stress levels, contributing to cancer risk.
Another important point to factor in is that improved screening methods and greater awareness are leading to more diagnoses at a younger age.
The Real Causes of Cancer
What are the exact causes of cancer? Dr. Ahmed pulls the curtain back on the science: “The three main fundamental causes of cancer are free radicals, chronic inflammation, and oxidative stress.”
1. Free Radicals: Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and lead to cancer. They are produced in the body through normal metabolic processes and external factors such as pollution, radiation, and smoking.
2. Chronic Inflammation: Persistent inflammation can damage healthy cells, tissues, and organs. This chronic state of inflammation can lead to DNA damage and increase the risk of cancer.
3. Oxidative Stress: Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. This can lead to cell and tissue damage, contributing to cancer development.
Which Cancers are Showing Up in Young Adults?
Dr. Ahmed points out that two cancers in particular are appearing in younger and younger patients: colorectal cancer and breast cancer.
- Colorectal Cancer: According to a 2022 study, colorectal cancer is diagnosed among young adults almost twice as often as it was in the 1990s.
- Breast Cancer: Early-onset breast cancer incidence has risen by almost 4% among U.S. women every year from 2016 to 2019.
Cancer Treatment for Younger Patients
Treatment plans for younger cancer patients often differ from those developed for older individuals. Cancer at a young age is generally more aggressive, necessitating aggressive treatment to reduce the risk of recurrence. Younger patients typically have fewer side effects from treatments compared to older patients, who may not be able to tolerate certain treatments due to toxicities.
Younger cancer patients also face unique challenges, including:
- Life Disruption: Cancer strikes at a time when individuals are supposed to be most active in their personal and professional lives.
- Social Isolation: Peers may not be empathetic or understanding, and treatments can affect immunity, making socialization risky.
- Financial Burden: Treatment expenses can be especially burdensome for those not yet well-established in their careers.
- Fertility Concerns: For those who have not started a family, fertility preservation becomes a significant concern.
According to Dr. Ahmed, the prognosis for younger cancer patients often depends on the cancer type and stage at diagnosis. Younger patients generally handle treatment better, have fewer side effects, and can receive treatments that are too risky for older individuals. However, they face a higher risk of recurrence due to their longer expected lifespan. Early detection is crucial for a better prognosis and potential cure.
“I would like to stress that early detection makes a tremendous difference in cancer treatment and prognosis. It can mean the potential for a cure for an early stage cancer rather than facing more advanced stages where treatment options may be limited,” Dr. Ahmed emphasizes.
Cancer Prevention for People of All Ages
The statistical trends for cancer diagnoses can be daunting. Combine them with the understanding of the very small role genetics plays in the development of these cancers, and it can seem like the modern lifestyle simply makes cancer inevitable, but there are things you can do to reduce your risk significantly. Dr. Ahmed recommends the following cancer prevention tips:
- Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: Prioritize a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Adhere to Screening Guidelines: Follow recommended screenings such as mammograms and colonoscopies.
- Be Vigilant About Health Changes: Consult a doctor promptly if unusual symptoms or lumps are noticed.
Dietary Recommendations to Prevent Cancer
“Thirty to thirty-five percent of cancers can be attributed to diet,” says Dr. Ahmed, “so what you put on your plate today does determine your risk of future cancer, to some extent.”
She goes on to explain, “Antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals and can help lower inflammation and prevent cancer. A diet rich in antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, fish, and legumes, can help reduce the risk of cancer.”
Foods rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties include:
- Fruits and Vegetables: These are high in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, carotenoids, and flavonoids. Examples include berries, citrus fruits, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts).
- Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are high in fiber and antioxidants, which can help reduce cancer risk.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, barley, and oats contain fiber and beneficial compounds that help lower cancer risk.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds provide healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants.
Avoid foods that increase free radicals and cause inflammation:
- Saturated Fats and Trans Fats: Found in fried foods, processed snacks, and baked goods, these fats can increase free radical production and inflammation.
- Red Meat: High consumption of red meat (beef, pork, lamb) is linked to an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Limit intake and choose lean cuts when possible.
- Sugary Drinks and Foods: Beverages and foods high in sugar can contribute to obesity and increase cancer risk. Avoid sugary sodas, candies, and desserts.
Prioritize a Healthy Lifestyle, Get Screened, and Be Vigilant
The rise in cancer diagnoses among younger people is concerning, but understanding the contributing factors and taking preventive measures can help mitigate risk. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, adhering to screening guidelines, and being vigilant about health changes, younger generations can significantly lower their cancer risk and improve their overall well-being.
“Cancer can develop at any age, and we are increasingly witnessing diagnoses among younger people,” Dr. Ahmed says. “My message to the younger generation is clear: prioritize a healthy lifestyle, adhere to recommended health guidelines for screenings such as mammograms and colonoscopies, and be vigilant about any changes in your health. If you notice something unusual, like a lump or persistent symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult your doctor promptly.”



